
RTK vs. PPK Drone Mapping. What’s the Difference.
Drone Mapping
Drone mapping and surveying have significant role in the new era of precision. With the advancement of technology, GPS correction techniques such as Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) and Post-Processing Kinematic (PPK) have emerged to enhance the accuracy and precision of GPS data collected by drones. Talking about the RTK and PPK, we can’t forget about the essential role of Ground Control Point (GCPs) in drone mapping. GCPs are physical markers placed on the ground with accurately known coordinates. They serve as reference points to improve the accuracy of geo-referenced images captured by drones. GCPs are traditionally used to achieve sub-centimeter level accuracy in mapping and surveying. However, setting up GCPs can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially in remote or complex terrains. This has led to the development of GPS correction technologies like RTK and PPK, which provide alternative methods to enhance GPS data accuracy without relying solely on GCPs.
Introducing Real-Time Kinematic (RTK)
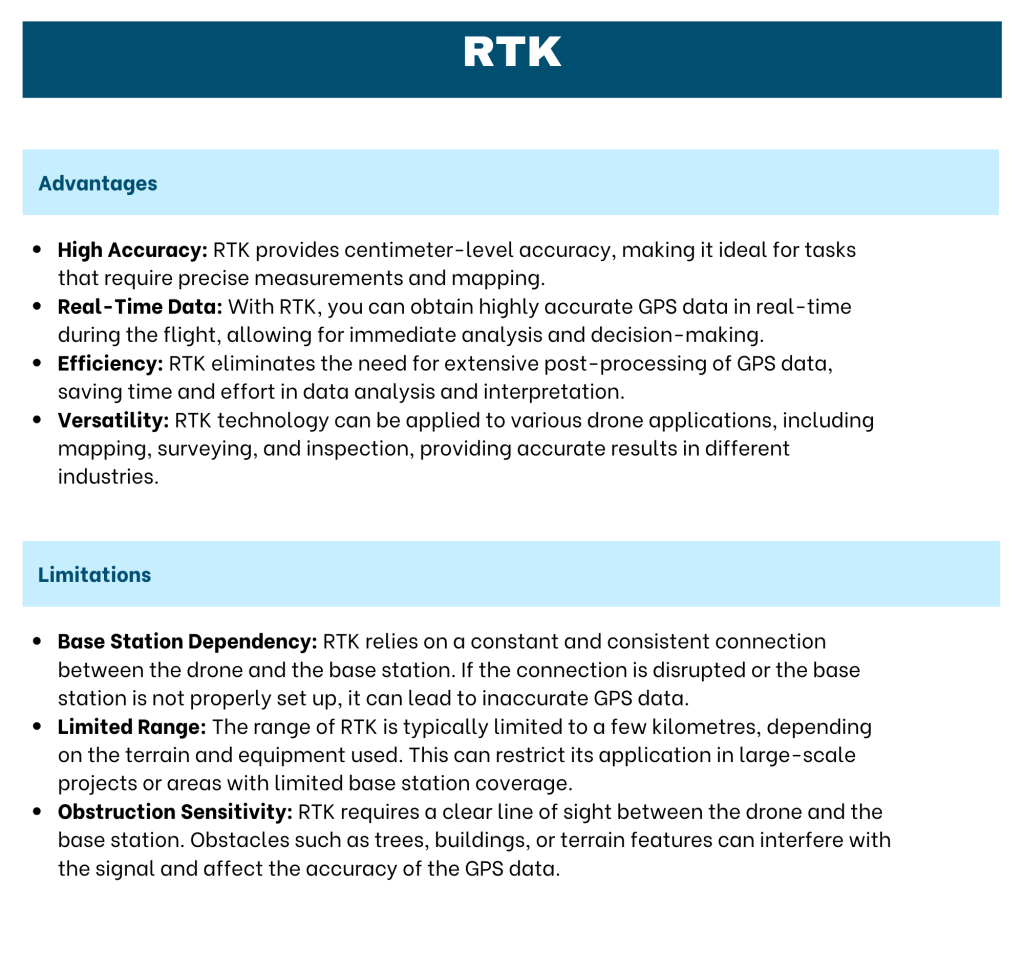
RTK is a GPS correction technique that provides real-time corrections to location data as the drone captures imagery. It involves the use of an onboard GNSS RTK receiver on the drone and a base station on the ground. The base station acts as a reference point for correcting the drone’s GPS data in real-time during the flight. RTK utilizes carrier phase tracking and atmospheric modeling techniques to compensate for atmospheric delays and improve the accuracy of the positioning data. The corrected data is transmitted to the drone in real-time, enabling highly accurate positioning during the flight.
Understanding Post-Processing Kinematic (PPK)
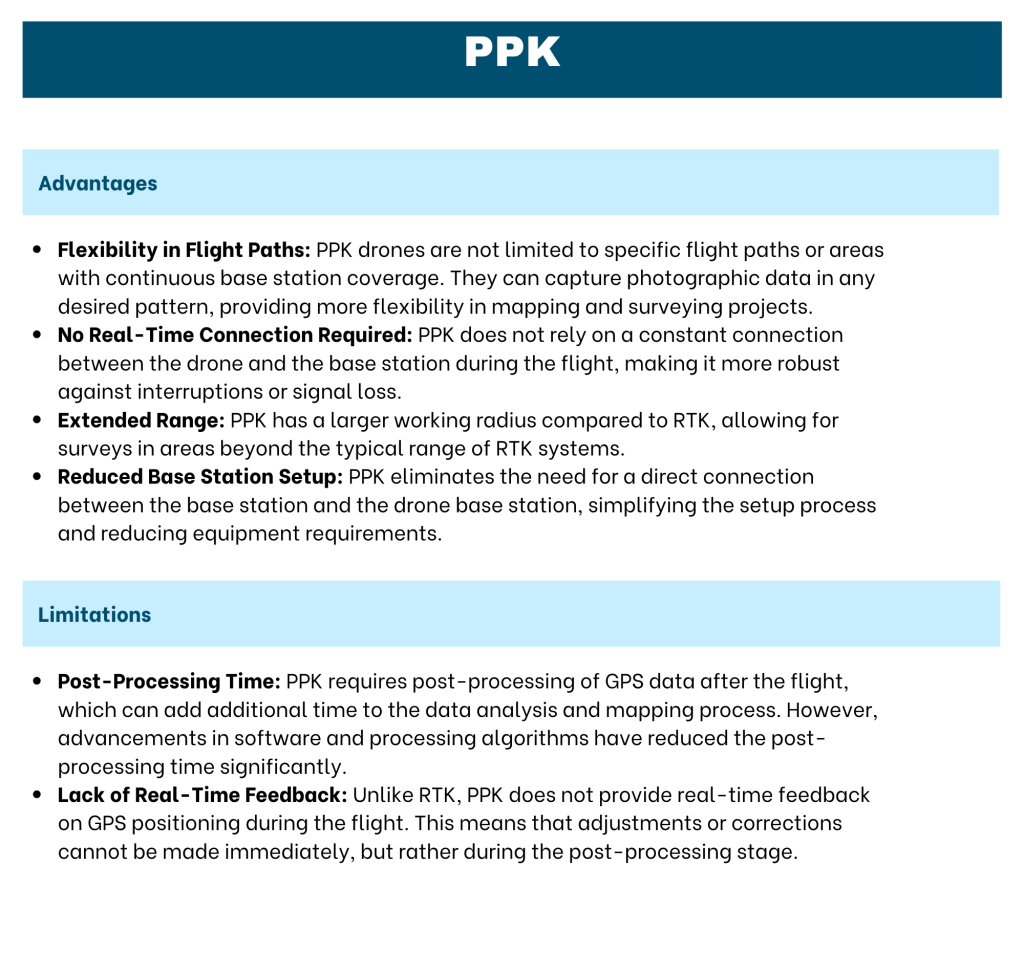
PPK is another GPS correction technique that improves the accuracy of GPS data collected by drones. Unlike RTK, PPK corrects the GPS data after the flight, during the post-processing stage. PPK drones are equipped with an onboard GNSS PPK receiver, which logs GPS data during the flight. Simultaneously, a base station or CORS network collects positional information. After the flight, the GPS data from the drone is matched with the base station data, and corrections are applied to enhance the accuracy of the drone’s GPS positioning.
Choosing the Right GPS Correction Technology
Choosing between RTK and PPK depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your project, the environment in which you will be operating, and the level of accuracy needed. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed

Ultimately, the choice between RTK and PPK depends on the specific requirements, constraints, and objectives of your mapping or surveying project. Assessing these factors will help you determine the most suitable GPS correction technology for your needs.
RTK and PPK are two GPS correction techniques that enhance the accuracy of GPS data collected by drones for mapping and surveying projects. While RTK provides real-time corrections during the flight, PPK corrects GPS data after the flight during the post-processing stage. Both techniques offer advantages and limitations, and the choice between RTK and PPK depends on various factors, including accuracy requirements, base station availability, obstacle density, time constraints, and project scale. By understanding the differences and considering these factors, you can choose the right GPS correction technology to achieve the level of accuracy and precision required for your specific drone mapping projects.
