
Enhancing Aerial Mapping Efficiency with Pix4D Mapper: Strategies for Optimal Ground Control Point Placement
Aerial mapping has brought a revolutionary transformation to various sectors, spanning survey construction, agriculture, urban planning, and environmental preservation industries. With the introduction of sophisticated software like Pix4D Mapper, the conversion of aerial imagery into precise maps and 3D models has become incredibly accessible. However, achieving ideal results mandates careful planning and strategic decision-making, particularly regarding the placement of ground control points (GCPs) on the ground, which serve as real reference points to enhance the accuracy of drone data. Drone Data loves GCPs
Without GCPs, you cannot ensure the accuracy of the drone data you have collected. Therefore, it is crucial to use GCPs correctly. While laying GCPs can be time-consuming, it is far more efficient and cost-effective than having to return to the site to re-fly and then lay GCPs again. Drone data thrives with the use of GCPs, so it is essential to utilize them properly from the outset.
Join us in this exploration as we uncover strategies for Pix4D Mapper users to enhance their aerial mapping efficiency through effective ground control point (GCP) placement. From understanding the importance of GCPs to actionable advice on selecting the best locations, we’ll guide you through the realm of aerial mapping with Pix4D Mapper.
Understanding the Importance of Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Ground Control Points serve as significant benchmarks with known coordinates on the Earth’s surface. By accurately pinpointing these points in aerial imagery within Pix4Dmapper software, users can georeference their maps and models, guaranteeing precise alignment with real-world coordinates. GCPs play a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy and reliability of aerial mapping outputs, making them indispensable assets for Pix4Dmapper users.
Strategies for Optimal GCP Placement
Quantity vs. Quality
While it might be tempting to scatter numerous GCPs across a survey area, quality often trumps quantity. Research suggests that the benefits of using more than 5-10 GCPs are minimal, particularly in smaller projects. Instead of spreading GCPs thin, focus on strategically placing them in key locations that provide maximum coverage and reference points. When laying GCPs, it’s important to know when enough is enough and when too little needs more. It’s about effectiveness and efficiency.
Strategic Distribution
Consider the topography and features of the survey area when selecting GCP locations. Aim to distribute GCPs evenly across the terrain, accounting for variations in elevation and land features. Placing GCPs evenly and correctly throughout the project area will allow for greater accuracy of the project. Select your GCP locations carefully, ensuring accessibility. It’s important to remember that while a single GCP provides a reference point, its accuracy is limited, and it relies on support from other GCPs to enhance the overall accuracy of the project.
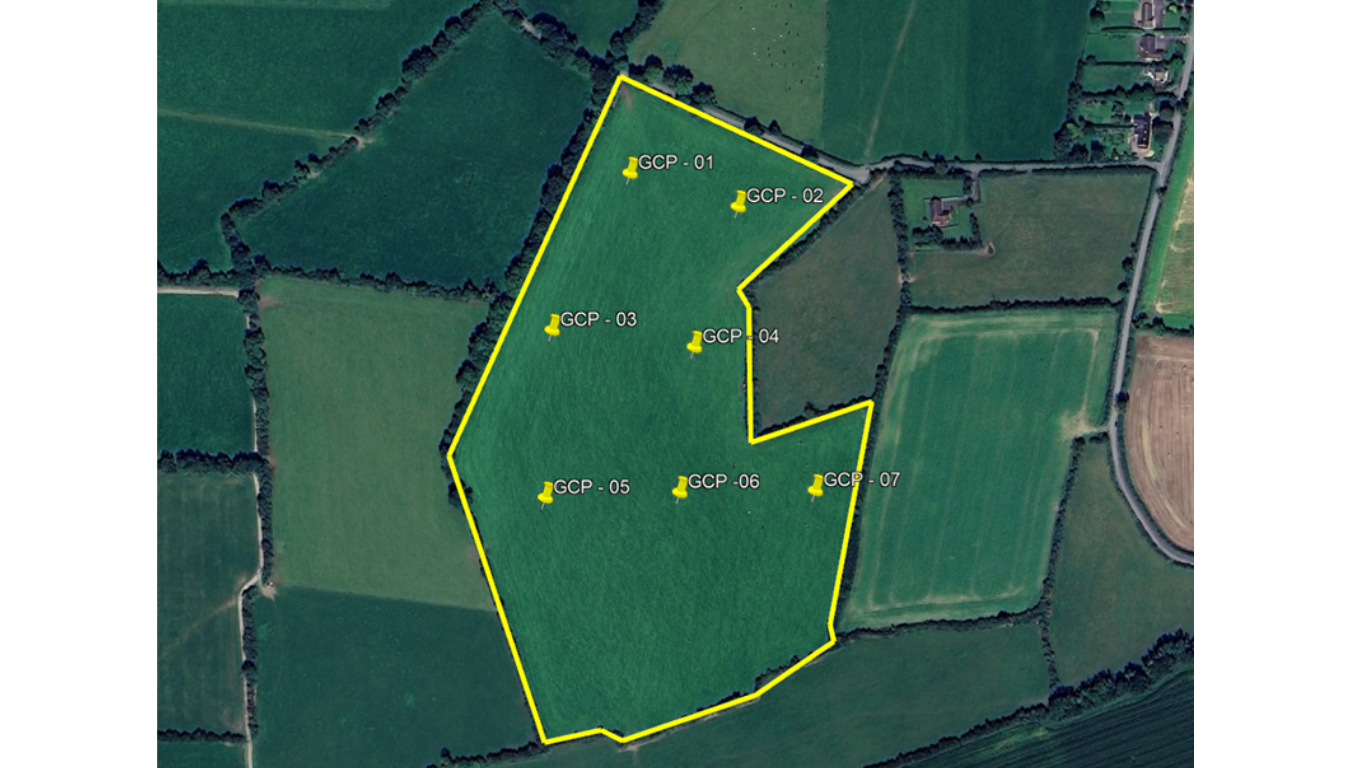
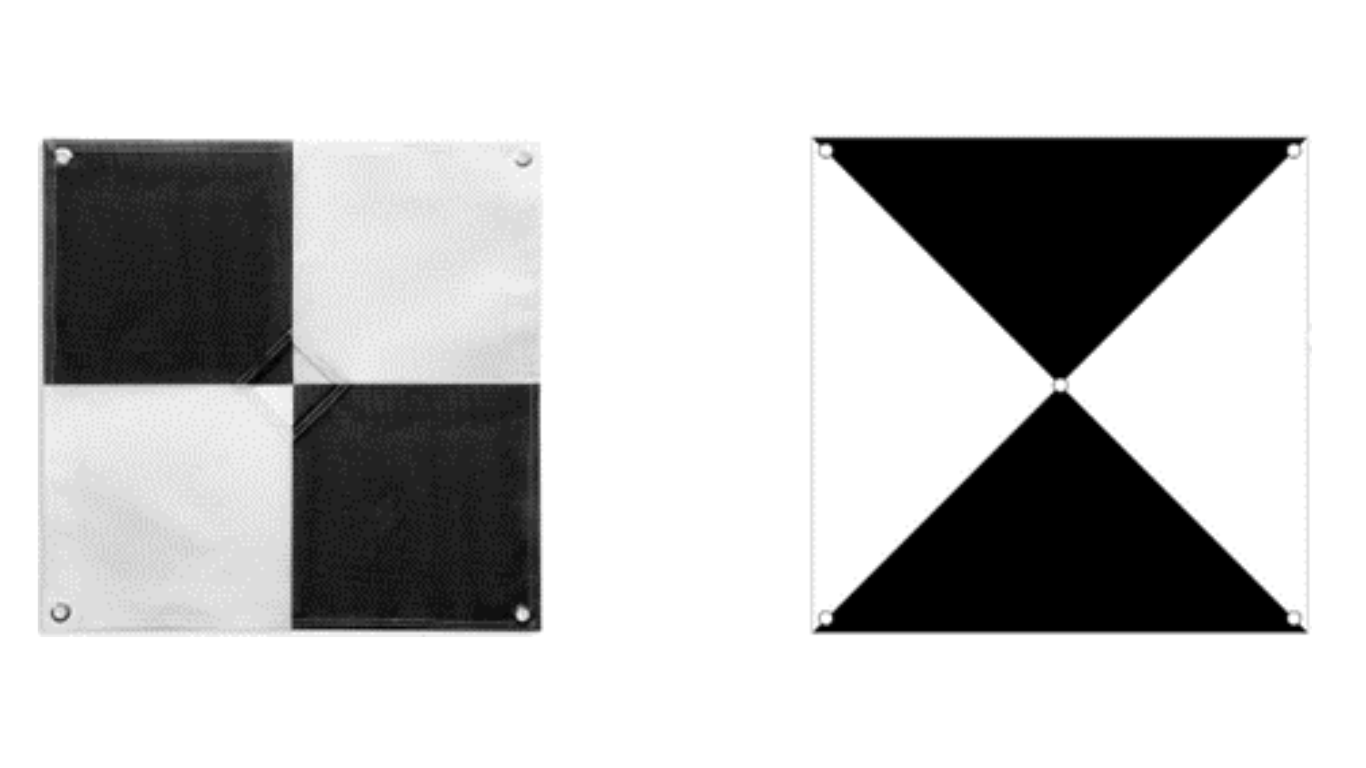
Visibility and Recognition
Choose GCP locations that are easily identifiable in aerial imagery. Opt for high-contrast markers or patterns, such as black-and-white squares or checkerboard patterns, that stand out against the surrounding landscape. Ensure that GCPs are visible from the drone’s flight altitude to facilitate accurate identification and georeferencing. It’s essential to consider your drone sensor’s capabilities in this process. Flying at an altitude of 100 meters AGL with a sensor of only 12MP may not provide clear and accurate data.
Accessibility and Safety
Prioritize GCP locations that are easily accessible and safe to reach during fieldwork. Avoid placing GCPs in hazardous or restricted areas that may pose risks to personnel or equipment. Plan GCP placement logistics in advance to streamline field operations and minimize downtime.
Consideration of Project Requirements
Ensure that your GCP workflow aligns with the specific requirements and objectives of each aerial mapping project. Factors such as project size, resolution, and accuracy goals will determine GCP placement. Collaborate with project stakeholders to identify key areas of interest, and then use your GCP workflow to lay GCPs accordingly. Remember, doubling your workload on the ground will also double your workload in the office during the processing stage.Top of Form
Enhancing Drone Mapping Accuracy with Ground Control Points
Ground Control Points play a vital role in significantly improving the accuracy of drone mapping. These points are crucial to surveyors as they are set with absolute accuracy. This means that a point correlates to a true value on the ground, such as a GPS coordinate, it’s a physical position. Relative accuracy, on the other hand, describes other points that can be found by scaling a map against these absolute coordinates.

Right Drone and Payloads for Accurate Surveying
Strategically positioned ground control points are essential, but having the right drones and camera payloads is equally crucial to completing the job effectively. The Mavic 3 Enterprise series, equipped with the RTK module, excels at rapid data capture with its high speeds and long-lasting batteries. Its feature for camera triggering and SD card storage significantly enhances efficiency. With a flight speed of up to 15m/s, it effortlessly captures and stores data, making it ideal for large sites. The improved sensor allows for smaller pixels, facilitating data processing in PIX4Dmapper without sacrificing quality.
For processing RGB data, we highly recommend PIX4Dmapper. Our workflow begins with meticulous planning, focusing on proper GCP selection and placement, without nailing these down (Please forgive the Pun), Only then do we proceed to data capture. After completing the project, we download the GCP file and drone data into PIX4Dmapper, initiating Step 1 of the processing. After Step 1 is complete we will then introduce the GCPs. This point onwards we can check our accuracy and correctly apply our GCPs into the project. When selecting the GCP in PIX4Dmapper its important to really zoom in as much as possible right down to the Pixel of the Image, to identify the exact location of where the tip of the pole was. Ideally you would have recorded a picture of where the tip of the pole was on the GCP. This can be used later for reference. Once you have selected all the GCPs you can then move on with the processing, confident that your accuracy have been achieved.
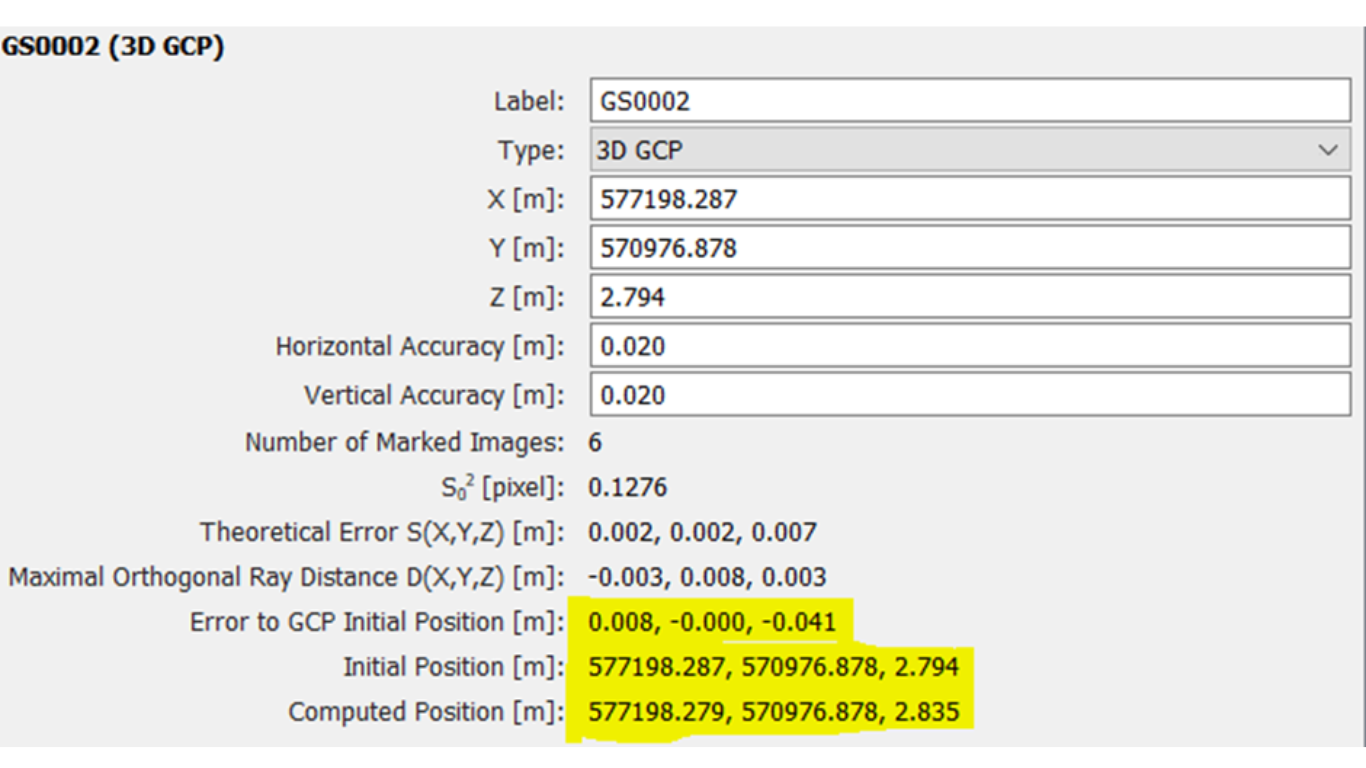
Efficient ground control point placement is essential for maximizing the accuracy and reliability of aerial mapping projects conducted with Pix4Dmapper. By employing strategic placement strategies and adhering to best practices, users can streamline their mapping workflows, minimize errors, and achieve exceptional results. Whether mapping vast landscapes or intricate urban environments, the strategic placement of GCPs is a cornerstone of successful aerial mapping with Pix4Dmapper. For further information on how to process Drone Data with the use of GCPs using PIX4Dmapper or any of the PIX4D software range, please do get in touch. As we run these courses regularly throughout the year.
Find out more here https://surveydrones.ie/pix4dsoftware/pix4d-mapper/
Offering three licence options:
Monthly Licence. – €290.00
Yearly Licence. – €2,900.00
Perpetual Licence. – €4690.00
Even though this guide provides comprehensive knowledge about the optimal placement of GCPs in aerial mapping projects using Pix4Dmapper, it is essential to remember that every project has unique requirements. It is advised to fine-tune the strategies discussed here according to the specific needs of your project to ensure the best results. By doing so, you can enhance the effectiveness of your aerial mapping operations and achieve the highest level of accuracy possible.
